木犀草素是有效的非小細胞肺癌模型L858R / T790M EGF受體突變和埃羅替尼抗性。
香港Z1,曹X,黎嗯,張Y,蘭L,周Y,潘X,沉L,尹Z,羅L.
作者信息

背景和目的:
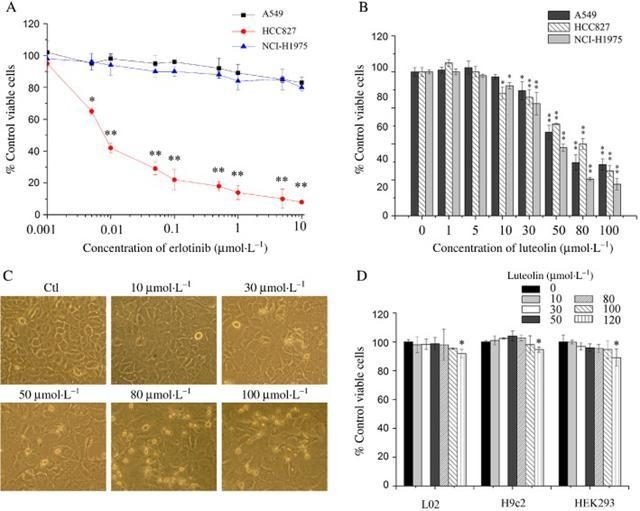
非小細胞肺癌(NSCLC)是世界上最常見的診斷的惡性腫瘤之一。 EGF受體的酪氨酸激酶結構域(的TKI),包括吉非替尼和厄洛替尼的小分子抑製劑,已被廣泛用於治療非小細胞肺癌。不幸的是,幾乎所有的患者在最初經歷了顯著的改善,而這些藥物,最終進展為獲得對TKIs阻力。因為有治療TKI耐非小細胞肺癌沒有有效的治療策略,我們評估木犀草素的影響,天然存在的類黃酮,對T790M突變NSCLC細胞。


實驗方法:
使用細胞計數試劑盒-8(CCK-8)測定木犀草素對非小細胞肺癌和正常細胞系的活力的影響進行了研究。木犀草素誘導的細胞凋亡是由二元FITC膜聯蛋白V / PI法檢測,並印跡被用來測量凋亡蛋白。免疫共沉澱來測定木犀草素對Hsp90的與突變體的EGF受體之間的相互作用的影響。使用Western印跡分析進行了研究木犀草素對Akt / mTOR途徑的效果。其在體內的抗腫瘤功效在小鼠異種移植模型進行了研究。

主要成果:
木犀草素作用於表皮生長因子受體L858R / T790M突變和埃羅替尼抗性的NSCLC既在細胞和動物水準顯著抗致瘤作用。機理上,木犀草素由與突變EGF受體抑製Hsp90的關聯引起的表皮生長因子受體的降解,並因此,防止了PI3K / Akt信號/ mTOR信號,這就造成了非小細胞肺癌細胞凋亡。

結論和意義:
木犀草素可以是用於非小細胞肺癌治療的潛在候選,特別是用於治療患者的獲得性耐葯厄洛替尼非小細胞肺癌。
?2014英國藥理學會。
原文來自於美國政府醫療網站
Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;171(11):2842-53. doi: 10.1111/bph.12610.
Luteolin is effective in the non-small cell lung cancer model with L858R/T790M EGF receptor mutation and erlotinib resistance.
Hong Z1,
Cao X,
Li N,
Zhang Y,
Lan L,
Zhou Y,
Pan X,
Shen L,
Yin Z,
Luo L.
Author information
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed malignancies in the world. Small-molecule inhibitors of the EGF receptor"s tyrosine kinase domain (TKIs), including gefitinib and erlotinib, have been widely used for treating NSCLC. Unfortunately, nearly all patients after initially experiencing a marked improvement while on these drugs, eventually progress to acquire resistance to TKIs. Because there is no effective therapeutic strategy to treat TKI-resistant NSCLC, we evaluated the effects of luteolin, a naturally occurring flavanoid, on T790M mutant NSCLC cells.
EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH:
The effect of luteolin on the viability of NSCLC and normal cell lines was investigated using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Luteolin-induced apoptosis was assessed by bivariate FITC-annexin V/PI assay, and Western blots were used to measured apoptotic proteins. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to determine the effect of luteolin on the interaction between Hsp90 and mutant EGF receptors. The effect of luteolin on the Akt/mTOR pathway was studied using Western blotting analysis. Its anti-tumour efficacy in vivo was examined in a mouse xenograft model.
KEY RESULTS:
Luteolin exerted significant anti-tumourigenic effects on the EGF receptor L858R/T790M mutation and erlotinib-resistant NSCLC both at the cellular and animal levels. Mechanistically, luteolin induced degradation of the EGF receptor by inhibiting the association of Hsp90 with the mutant EGF receptor, and, therefore, prevented PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling, which resulted in NSCLC cell apoptosis.
CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATIONS:
Luteolin may be a potential candidate for NSCLC therapy, especially for treatment of patients with acquired erlotinib-resistant NSCLC.
? 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.