每年的7月28日為世界肝炎日。肝炎是肝臟炎症,最常見的原因是病毒感染。主要有甲、乙、丙、丁、戊五種類型。尤其是乙型肝炎和丙型肝炎可使數億人罹患慢性病,並且二者是發生肝硬化和肝癌的最常見原因。目前,在肝炎防治領域,最需要解決的就是檢測和治療覆蓋率低這一問題。為實現2030年全球肝炎消除目標,世衛組織將今年世界肝炎日的活動主題定為「檢測·治療·肝炎」。
▼

下面是公眾需要了解的
關於肝炎的十條核心資訊
01
B肝與C肝是重大衛生問題
全球範圍內,有3.25億人是慢性B肝和C肝感染者,其流行規模是愛滋病的9倍。
B肝與C肝是肝癌發生的根本原因
02
慢性B肝和C肝感染可能在幾年、甚至是幾十年時間內都沒不會表現出癥狀。 B肝與C肝會緩慢地、悄悄地損害肝臟,最終導致肝癌。
03
及時診斷和治療B肝與C肝可以
挽救生命
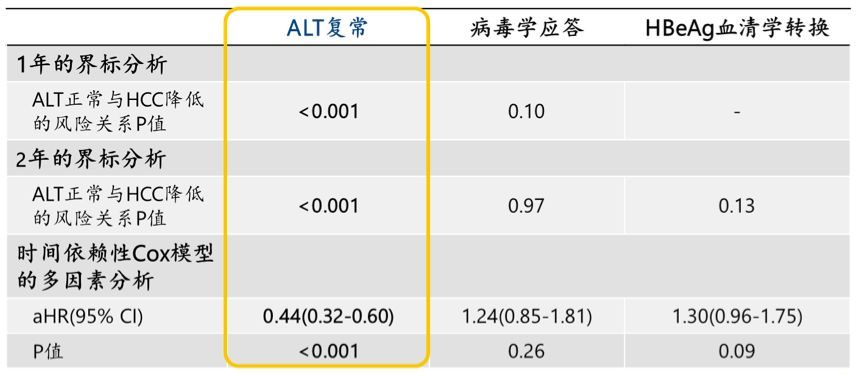
至少有60%的肝癌病例的發生源於B肝與C肝的晚診斷與晚治療(43%源於B肝,17%源於C肝)。戰勝肝炎等於戰勝肝癌。
病毒性肝炎引起衰竭性疾病,同時
也給家庭帶來沉重負擔
04
許多肝炎病毒感染者同時受到其他疾病的困擾,如糖尿病,抑鬱以及高血壓,不但影響了他們的生活品質,也導致了經濟壓力。
05
由於缺少全球關注,病毒性肝炎
已經成為主要傳染病殺手
每年,病毒性肝炎引起導致134萬人死亡(多於HIV或瘧疾所致死亡人數),這使得病毒性肝炎成為列結核之後的第二大傳染病殺手。每天,有超過3600人死於病毒性肝炎。
在過去的15年間,有越來越多的人
死於病毒性肝炎
06
肝炎導致的死亡數增加了22%,同時其他傳染病(如HIV,結核和瘧疾)死亡人數均已下降。
07
同時,有更多人新感染上肝炎
每天,將近有4800名成人新感染上C肝。(每年175萬名成人,比每年新感染HIV或者瘧疾的人要多),每年B肝新發感染人數的確切數字未知。
肝炎侵襲最脆弱的人群
08
超過90%的B肝新發感染通過母嬰傳播在嬰幼兒時期發生。有一些人處在B肝與C肝感染的高風險中,包括注射吸毒人群,男男同性性行為人群,接受過紋身、針刺與針灸的人,B肝感染者的伴侶,以及醫療工作者等。
09
肝炎可以預防,診斷,治療,
甚至治癒
B肝疫苗預防新發感染的有效率為95%。針對B肝,人們需要接受檢測,如果結果為陽性,在需要的情況下,接受終身治療。 但是許多感染者並不需要治療,但是要定期檢查。針對C肝,人們需要接受檢測,提供治療,可在2-3個月內完全治癒C肝感染。
你可以為消除肝炎盡一份力
10
在2018世界肝炎日發聲,促進預防接種、及時檢測和治療服務的全民覆蓋。





點擊「閱讀原文」,了解更多資訊
Test. Treat. Hepatitis
The July 28th is the world"s Hepatitis Day. Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. The most common cause is viral infection. There are five main types: Class A, B, C, D and E. In particular, hepatitis B and hepatitis C can cause hundreds of millions of people suffering from chronic diseases, and the combinations infection is the most common cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Currently, in the hepatitis prevention and treatment area, the low coverage of testing and treatment is the most important gap to be addressed. In order to achieve the global elimination goals by 2030, for the 2018 event, WHO Therefore recommends the theme: "Test. Treat. Hepatitis".

1. Viral hepatitis B and C are major health challenges.
Affect 325 million people globally. The epidemic is 9 times larger than the global HIV epidemic.
2. Viral hepatitis B and C are root causes of liver cancer.
These are chronic infections that may not show symptoms for a long period, sometimes years or decades. Hepatitis B and C slowly and silently damage the liver, eventually causing cancer.
3. Timely testing and treatment of viral hepatitis B and C can save lives.
At least 60% of liver cancer cases are due to late testing and treatment of viral hepatitis B and C (43% due to hepatitis B, and 17% due to hepatitis C).5 Defeating hepatitis means defeating liver cancer.
4. Viral hepatitis causes debilitating diseases and also places a huge economic burden on families.
Many people living with hepatitis also suffer other illnesses such as diabetes, depression and hypertension, which affect their quality of life and cause financial stress.
5. Viral hepatitis has become a major killer due to a lack of global attention.
Every year it causes 1.34 million deaths (more deaths than are caused by HIV or malaria), making viral hepatitis the second biggest killer after tuberculosis. Every day, more than 3600 people die of viral hepatitis.
6. Over the past 15 years, more and more people have been dying of viral hepatitis.
The number of deaths caused by hepatitis has risen by 22%, while mortality due to other major infectious diseases, such as HIV, tuberculosis and malaria, has all declined.
7. At the same time, people are becoming newly infected with hepatitis.
Every day, nearly 4800 adults become newly infected with hepatitis C (1.75 million adults a year, which is more than the number of new infections from HIV or malaria). The exact number of new hepatitis B infections is unknown.
8. Hepatitis attacks the most vulnerable.
Over 90% of new hepatitis B infections occur through mother-to-child transmission and during early childhood. But other groups are also at higher risk of both hepatitis B and C, including people who inject drugs; men who have sex with men; people who have had tattoos or acupuncture; partners of people living with hepatitis B; and health care workers.
9. Hepatitis can be prevented, diagnosed,7 treated8 and even cured.
The hepatitis B vaccine is 95% effective in preventing new infections. For hepatitis B, people should be tested and, if positive and needed, provided with lifelong treatment.
Many patients will not require treatment, but should be regularly checked. For hepatitis C, people should be tested, then provided with treatment to be completely cured of the infection within 2–3 months.
10. You can help eliminate hepatitis.
Speak up on World Hepatitis Day 2018 to promote universal health coverage for immunization, timely testing and treatment services for viral hepatitis infections.